Configure a Service with Multiple Endpoints to External Services
Journey Manager (JM) The transaction engine for the platform. | System Manager / DevOps | All versions This feature is related to all versions.
Manager allows you to create new and configure existing services. However, as we create services in Manager that integrate with external sources via Web Service or REST REST or RESTful API design (Representational State Transfer) is designed to take advantage of existing protocols. While REST can be used over nearly any protocol, it usually takes advantage of HTTP when used for Web APIs., we typically find that the external service endpoint and credentials change between Manager environments such as development, test, and production. Alternatively, you may have created a mock service endpoint for use during early development phases and want the ability to easily switch between the mock service and the genuine service for debugging and to verify expected results.
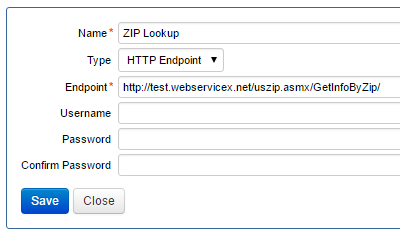
The best approach to managing multiple endpoint configurations is to utilize service connections. Consider the following example. We have a requirement to build a Dynamic Data service for use by forms that takes a US Zip Code and returns the City, State, Area Code, and Time Zone. This service will call out to an external APIApplication Programming Interface. to retrieve this information. The external service provider has exposed a test service for use in development and test environments, which we will use until we deploy to the production server.
To configure a service with multiple endpoints:
- Create a service connection for the genuine endpoint using the generic HTTP Endpoint type. Enter the name and endpoint URIREST or RESTful API design (Representational State Transfer) is designed to take advantage of existing protocols. While REST can be used over nearly any protocol, it usually takes advantage of HTTP when used for Web APIs..
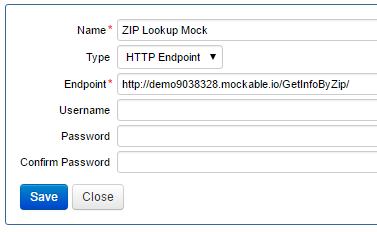
- Create another service connection to point to a mock platform, for example, mockable.io. As you are developing this service, you want to access this mock endpoint to control the response format and verify the behavior of the service.
- Create a new dynamic data service,
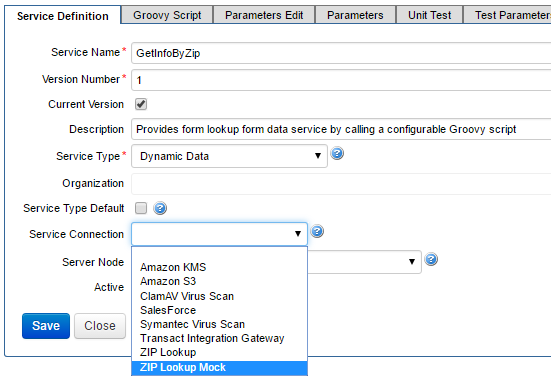
GetInfoByZip, to facilitate the dynamic data calls from forms or other components. - Configure the service.
- Select the service connection you want to use to develop and test your service. You should start with the ZIP Lookup Mock service connection because it points to the mock testing environment.
- Click the Groovy Script tab and update the script which retrieves the service connection from the service definition object and validate that it is configured correctly.
- Select the genuine service connection, for example, ZIP Lookup, in the Service Definition after you have tested the service.
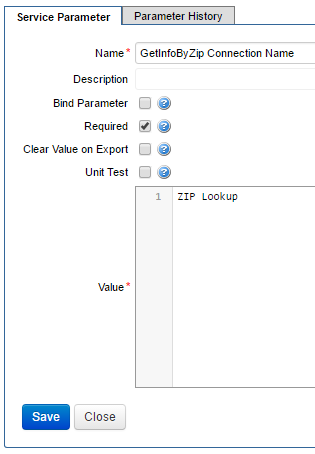
- Create a service parameter for each of the remote services, that stores the name of the service connection to use if your Groovy service is required to call several remote services in a single execution.
- Update your Groovy script to retrieve each service connection by name and then execute your remote call as normal.
- Migrate the service to promote it into another environment.
You can also add authentication credentials if it is required.
Transact Fluent API
import com.avoka.tm.vo.*
String invoke(SvcDef svcDef, Txn txn, HttpServletRequest request, User user) {
...
def serviceConnection = svcDef.svcConn
if(!serviceConnection){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"No Service Connection defined for this service.")
}
def endPoint = serviceConnection.endpoint
if(!endPoint){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"No endpoint defined for the service connection.")
}
...
}Core Transact API
def serviceConnection = serviceDefinition.connection
if(!serviceConnection){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"No Service Connection defined for this service.")
}
def endpoint = serviceConnection.endpointValue
if(!endpoint){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"No endpoint defined for the service connection.")
}
Update the script with the remote request, apply basic authentication credentials, if present, and execute the call against the mock endpoint before marshaling the response.
Transact Fluent API
import com.avoka.tm.vo.*
String invoke(SvcDef svcDef, Txn txn, HttpServletRequest request, User user) {
...
Map params = [:]
...
String username = svcDef.paramsMap.username
String password = svcDef.paramsMap.password
HttpResponse response = new GetRequest(endPoint)
.setParams(params)
.setBasicAuth(username, password)
.execute()
...
}Core Transact API
// Create the remote request
def remoteRequest = new GetRequest(endpoint)
// If auth details provided, set them in the remote request
if(serviceConnection.username){
remoteRequest.setBasicAuth(serviceConnection.username,
serviceConnection.password)
}
// Now execute the remote call
remoteRequest.setParams(["USZip": zipInput])
def response = remoteRequest.execute()
Transact Fluent API
import com.avoka.tm.query.*
String invoke(SvcDef svcDef, Txn txn, HttpServletRequest request, User user) {
...
def zipConnectionName = svcDef
.paramsMap
.get('GetInfoByZip Connection Name')
if(!zipConnectionName){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Missing parameter value for: GetInfoByZip Connection Name")
}
SvcConn svcConn = new SvcConnQuery()
.setName(zipConnectionName)
.firstValue();
if(!svcConn){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"No Service Connection defined for this service.")
}
...
}Core Transact API
// Check the endpoint parameter is defined
def zipConnectionName = serviceParameters.get('GetInfoByZip Connection Name')
if(!zipConnectionName){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Missing parameter value for: GetInfoByZip Connection Name")
}
// Ensure that a Service Connection is selected
def serviceConnection = new com.avoka.fc.core.dao.ServiceConnectionDao().getServiceConnectionForName(zipConnectionName)
if(!serviceConnection){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"No Service Connection defined for this service.")
}
If service connections are referenced by parameter values in this manner, they will not be exported into the service archive and must be manually created in other environments.
Make sure the genuine service connection is selected before export and you select the Preserve Existing Service Connections option during the import.
Use consistent naming of service connections between environments to avoid any manual reconfiguration each time you import a service from one environment to another. You can per-configure the service connections in each environment or wait until the service connection is imported into each environment and modify the configurations at that point. In production environments, you can configure the endpoint to point to the live endpoint with production credentials, if required.
Next, learn how to remove a service.