Use a Build-in Camera in TransactField App
TransactField AppThis topic is related to TransactField App. | Deprecated in 21.11 This feature was deprecated in 21.11.
There are some form functions available only through native apps, the inbuilt camera being one of them. HTML forms can have the user upload images from the device's camera roll as attachments, but the mobile app can go further and have the user snap a photo from the form. The mobile App can also handle bar codes in a way not available to HTML forms accessed through a web browser.
Barcodes
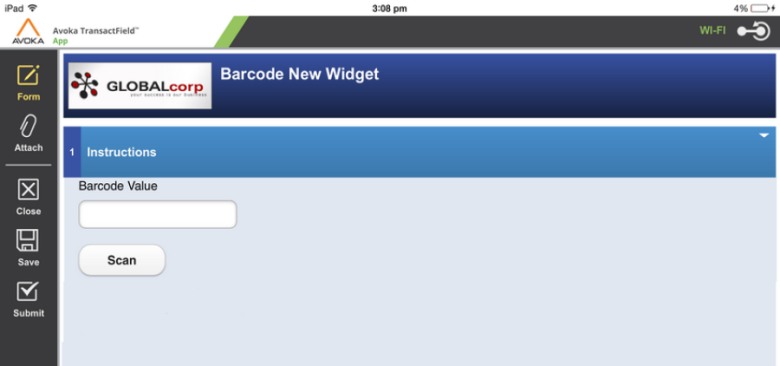
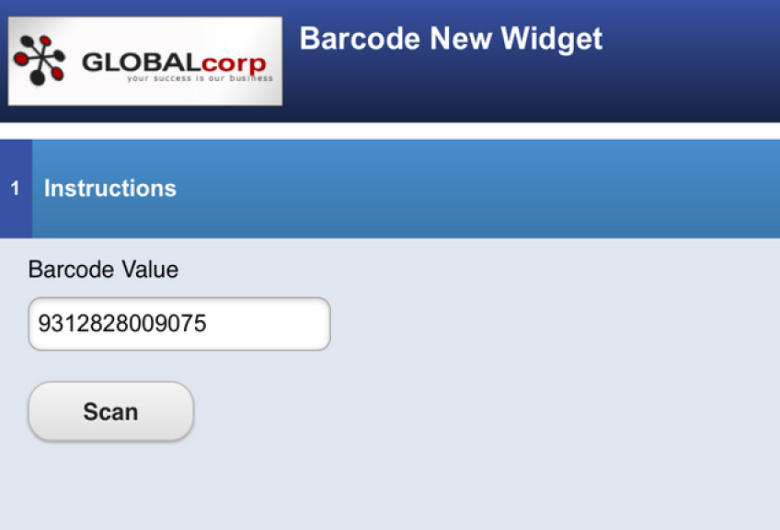
The Temenos Journey Manager platform allows a form to have a barcodeBarcode is a machine-readable code in the form of numbers and a pattern of parallel lines of varying widths, printed on a commodity and used especially for stock control. button, so a device camera reads a barcode and its data is returned to the form. This eliminates the need for a user to submit the form for the barcode to be deciphered, because it is now done within TransactField App.
The barcode must be positioned over the semi-transparent red line, the device must be moved close enough that the image focuses and when the software finds that it can read the image, the user is taken back to the form with the Barcode Value field filled in with the value of the code.
The barcode scanner module behaves slightly differently in Android and Windows phone devices: there may not be the red line display (to simulate a laser scanner) and the camera's focus may operate differently.
Note: for iPads, iPhones and iPod Touches — the camera's auto-focus software does not work in the usual way, by tapping on a point in the preview window. The only real control, other than physically moving the whole device, is the "Cancel" button at the bottom of the window. The user does not have a shutter control to take the picture in the usual way. Instead the App goes back to the form when it has successfully read the barcode.
Supported Formats
TransactField App supports the following AIMAssociation for Automatic Identification and Mobility (AIM) is an industry trade group that developed and standardized bar codes, Automatic identification and data capture. formats:
UPC-A and UPC-E
The Universal Product Code or UPC barcode was the first bar code symbology widely adopted. Its birth is usually set at April 3, 1973, when the grocery industry formally established UPC as the standard bar code symbology for product marking. Foreign interest in UPC led to the adoption of the EAN code format, similar to UPC, in December 1976.
Code 93
Code 93 offers higher information density for alphanumeric data than either Code 39 or Code 128. Code 93 is used primarily by Canada Post to encode supplementary delivery information. Every symbol includes two check characters.
Codabar
Codabar can encode the digits 0 through 9, six symbols (-:.$/+), and the start/stop characters A, B, C, D, E, *, N, or T.
Data Matrix
Data Matrix is a two-dimensional matrix symbology containing dark and light square data modules. It has a finder pattern of two solid lines and two alternating dark and light lines on the perimeter of the symbol. A two-dimensional imaging device such as a CCD camera is necessary to scan the symbology. Data Matrix is used for small item marking applications using a wide variety of printing and marking technologies.
EAN-8 and EAN-13
See the UPC variants above
Code 128
Code 128, a very high-density barcode symbology, is currently used extensively world wide in shipping and packaging industries. The symbol can be as long as necessary to store the encoded data. It is designed to encode all 128 ASCII characters, and will use the least amount of space for data of 6 characters or more of any 1-D symbology.
RSS-14
RSS (Reduced Space Symbology) is now called GS-1 Databar. Seehttp://www.databar-barcode.info/ Example: Databar-14:
Aztec
Partially supported.Aztec Code is a two-dimensional matrix symbology containing dark and light square data modules. It has a finder pattern of concentric square rings centered on a single dark module located in the center of the symbol. A two-dimensional imaging device such as a CCD camera is necessary to scan the symbology. Aztec Code is used for small item marking applications using a wide variety of printing and marking technologies, and is also well suited for displays of cell phones and other mobile devices.
Code 39
Code 39, pioneered by the defense and automotive industries, is an alphanumeric bar code. The symbol can be as long as necessary to store the encoded data. It is designed to encode 26 uppercase letters, 10 digits and 7 special characters. It can be extended to code all 128 ASCII characters by using a two character coding scheme.
ITF
ITF barcodes, also known as Interleaved 2 of 5 barcodes, encode 14 numeric digits and are generally used for the packaging level of products. Since they can deal with high printing tolerances, ITF is a good choice when barcodes need to be printed on corrugated cardboard.
RSS Expanded
RSS Expanded is capable of storing 74 numeric or 41 alphabetic characters and is normally used in point of sale retail applications. See http://www.bardecode.com/en1/rss-expanded-examples/
We support most variants.
PDF 417
Current support needs further work. PDF417 is a two-dimensional, multi-row symbology designed to be scanned by laser scanners and linear CCD scanners and used to encode data files with hundreds or thousands of characters in a laser scannable symbol. PDF417 is used in a variety of applications, primarily transport, identification cards, and inventory management.
QR Code
QR Code is a two-dimensional matrix symbology containing dark and light square data modules. It has position detection patterns on three of its four corners and features direct encodation of the Japanese Kana-Kanji character set. A two-dimensional imaging device such as a CCD camera is necessary to scan the symbology. Although initially used for tracking parts in vehicle manufacturing, QR Codes are now used in a much broader context, including both commercial tracking applications and convenience-oriented applications aimed at mobile phone users (known as mobile tagging).
This is the recommended barcode format. Our testing shows it is the most suitable for mobile.
Next, learn how to view history in TransactField App.